Avian influenza – Virus 2024
Avian Influenza: Understanding the Virus and Its Impact on Global Health
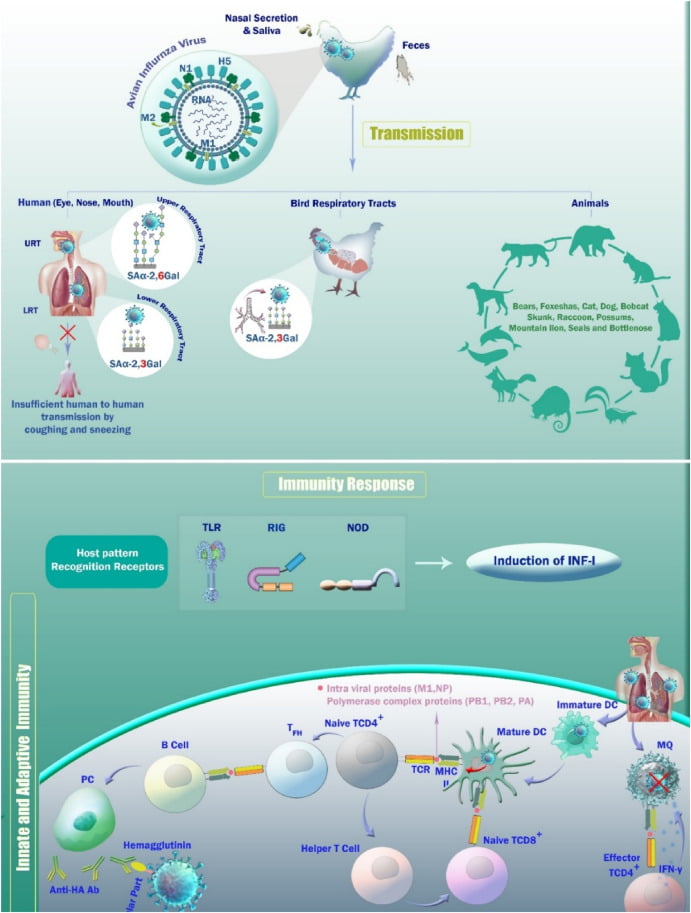
Avian influenza, also known as bird flu, is a highly contagious and potentially deadly viral disease that affects birds. However, it can also infect humans, posing a significant threat to global health. In this article, we will delve into the details of the virus, its transmission, symptoms, and the measures being taken to prevent its spread.
What is Avian Influenza?
Avian influenza is a viral disease caused by the influenza A virus, which is typically found in birds. The virus is highly contagious and can spread quickly among bird populations, causing significant mortality rates. There are several subtypes of the virus, but the most common ones that affect humans are H5N1 and H7N9.
Transmission of Avian Influenza
Avian influenza is primarily transmitted from birds to humans through direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. This can occur through:
1. Direct Contact: Handling or consuming undercooked or raw poultry products, such as eggs or meat, can expose individuals to the virus.
2. Indirect Contact: Touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus, such as feathers, feces, or saliva, can also lead to infection.
3. Airborne Transmission: In rare cases, the virus can spread through the air, particularly in crowded areas where birds are present.
Symptoms of Avian Influenza in Humans
The symptoms of avian influenza in humans are similar to those of seasonal flu, but they can be more severe and even life-threatening. Common symptoms include:
1. Fever: High fever, often accompanied by chills.
2. Cough: Dry, persistent cough.
3. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing.
4. Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired or weak.
5. Headache: Severe headache.
6. Muscle Pain: Muscle aches or pains.
Prevention and Control Measures
To prevent the spread of avian influenza, several measures are being taken globally:
1. Vaccination: Vaccination programs are being implemented for poultry and other birds to reduce the risk of transmission.
2. Quarantine: Infected birds are quarantined to prevent the spread of the virus.
3. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Healthcare workers and individuals handling birds wear PPE, such as masks, gloves, and gowns, to prevent transmission.
4. Surveillance: Monitoring of bird populations and surveillance systems are in place to detect and respond to outbreaks quickly.
5. Public Awareness: Public awareness campaigns are being conducted to educate people about the risks and prevention measures.
Global Response to Avian Influenza
The global response to avian influenza has been swift and coordinated. International organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), are working closely with national governments to:
1. Monitor Outbreaks: Track and monitor outbreaks to prevent the spread of the virus.
2. Develop Vaccines: Develop and distribute vaccines to protect birds and humans.
3. Enhance Surveillance: Strengthen surveillance systems to detect and respond to outbreaks quickly.
4. Provide Support: Provide technical and financial support to affected countries to help them contain outbreaks.
Conclusion
Avian influenza is a significant threat to global health, and it is essential that we take proactive measures to prevent its spread. By understanding the virus, its transmission, and symptoms, we can take steps to protect ourselves and our communities. The global response to avian influenza has been commendable, and continued collaboration and coordination are crucial to containing and preventing outbreaks.